LinkedList
LinkedList (əlaqəli siyahı) data strukturu, node-lardan (düyünlərdən) ibarət olan və hər bir node-un özündən sonrakı node-a (və bəzən də əvvəlki node-a) referans saxladığı bir data strukturudur. LinkedList-lər, elementlərin dinamik şəkildə əlavə edilməsi və silinməsi üçün effektiv bir vasitədir.
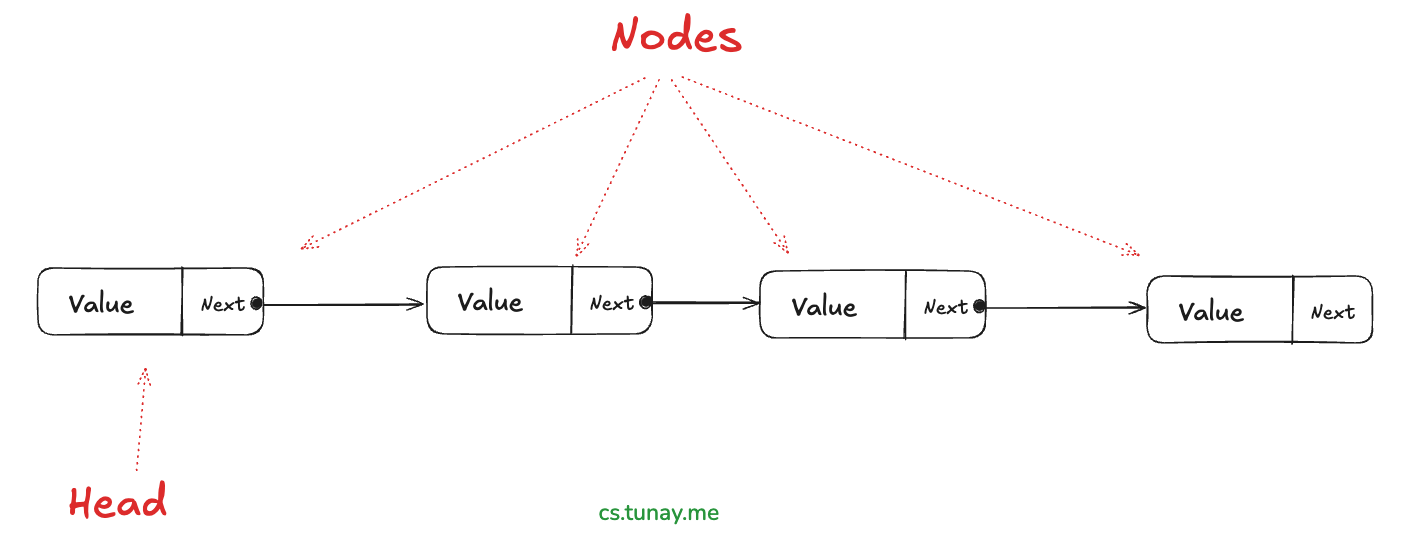
LinkedList-in Əsas Xüsusiyyətləri
- Node-Based: Hər bir element (node) data və pointer(s) saxlayır
- Dynamic Size: Ölçüsü dinamik olaraq dəyişə bilir
- Non-Contiguous Memory: Elementlər yaddaşda ardıcıl yerləşmir
- Insertion/Deletion: Elementlərin əlavə edilməsi və silinməsi effektivdir
- Random Access: Birbaşa indeks ilə elementə çatmaq mümkün deyil
LinkedList-in Növləri
1. Singly LinkedList (Tək İstiqamətli Əlaqəli Siyahı)
Singly LinkedList-də hər bir node özündən sonrakı node-a bir referans saxlayır. Bu, bir istiqamətdə hərəkət etməyə imkan verir.
2. Doubly LinkedList (İki İstiqamətli Əlaqəli Siyahı)
Doubly LinkedList-də hər bir node həm özündən sonrakı, həm də özündən əvvəlki node-a referans saxlayır. Bu, hər iki istiqamətdə hərəkət etməyə imkan verir.
3. Circular LinkedList (Dairəvi Əlaqəli Siyahı)
Circular LinkedList-də son node birinci node-a referans saxlayır, beləliklə dairəvi bir struktur yaranır. Bu, həm singly, həm də doubly ola bilər.
LinkedList-in Java-da İmplementasiyası
Singly LinkedList İmplementasiyası
Koda bax
public class SinglyLinkedList<T> {
// Node class
private static class Node<T> {
T data;
Node<T> next;
public Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Head node
private Node<T> head;
private int size;
// Constructor
public SinglyLinkedList() {
head = null;
size = 0;
}
// LinkedList-in ölçüsünü əldə etmək
public int size() {
return size;
}
// LinkedList-in boş olub-olmadığını yoxlamaq
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// LinkedList-in əvvəlinə element əlavə etmək
public void addFirst(T data) {
Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(data);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
size++;
}
// LinkedList-in sonuna element əlavə etmək
public void addLast(T data) {
Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
} else {
Node<T> current = head;
while (current.next != null) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
}
size++;
}
// Verilmiş indeksə element əlavə etmək
public void add(int index, T data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size);
}
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(data);
Node<T> current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
size++;
}
// LinkedList-in əvvəlindəki elementi silmək
public T removeFirst() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("LinkedList is empty");
}
T data = head.data;
head = head.next;
size--;
return data;
}
// LinkedList-in sonundakı elementi silmək
public T removeLast() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("LinkedList is empty");
}
if (size == 1) {
T data = head.data;
head = null;
size = 0;
return data;
}
Node<T> current = head;
while (current.next.next != null) {
current = current.next;
}
T data = current.next.data;
current.next = null;
size--;
return data;
}
// Verilmiş indeksdəki elementi silmək
public T remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size);
}
if (index == 0) {
return removeFirst();
}
Node<T> current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
T data = current.next.data;
current.next = current.next.next;
size--;
return data;
}
// Verilmiş indeksdəki elementi əldə etmək
public T get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size);
}
Node<T> current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
return current.data;
}
// Verilmiş indeksdəki elementi dəyişdirmək
public void set(int index, T data) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size);
}
Node<T> current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
current.data = data;
}
// LinkedList-i çap etmək
public void printList() {
Node<T> current = head;
System.out.print("LinkedList: ");
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " -> ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
SinglyLinkedList<Integer> list = new SinglyLinkedList<>();
// Elementlər əlavə etmək
list.addLast(10);
list.addLast(20);
list.addLast(30);
list.addFirst(5);
list.add(2, 15);
list.printList(); // LinkedList: 5 -> 10 -> 15 -> 20 -> 30 -> null
// Elementləri silmək
System.out.println("Removed first: " + list.removeFirst());
System.out.println("Removed last: " + list.removeLast());
System.out.println("Removed at index 1: " + list.remove(1));
list.printList(); // LinkedList: 10 -> 20 -> null
// Elementləri əldə etmək və dəyişdirmək
System.out.println("Element at index 0: " + list.get(0));
list.set(0, 100);
list.printList(); // LinkedList: 100 -> 20 -> null
}
}
Doubly LinkedList İmplementasiyası
Koda bax
public class DoublyLinkedList<T> {
// Node class
private static class Node<T> {
T data;
Node<T> prev;
Node<T> next;
public Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Head and tail nodes
private Node<T> head;
private Node<T> tail;
private int size;
// Constructor
public DoublyLinkedList() {
head = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
}
// LinkedList-in ölçüsünü əldə etmək
public int size() {
return size;
}
// LinkedList-in boş olub-olmadığını yoxlamaq
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// LinkedList-in əvvəlinə element əlavə etmək
public void addFirst(T data) {
Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(data);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = head;
head.prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
}
size++;
}
// LinkedList-in sonuna element əlavə etmək
public void addLast(T data) {
Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(data);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.prev = tail;
tail.next = newNode;
tail = newNode;
}
size++;
}
// Verilmiş indeksə element əlavə etmək
public void add(int index, T data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size);
}
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size) {
addLast(data);
return;
}
Node<T> newNode = new Node<>(data);
Node<T> current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = current;
newNode.prev = current.prev;
current.prev.next = newNode;
current.prev = newNode;
size++;
}
// LinkedList-in əvvəlindəki elementi silmək
public T removeFirst() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("LinkedList is empty");
}
T data = head.data;
if (size == 1) {
head = null;
tail = null;
} else {
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
}
size--;
return data;
}
// LinkedList-in sonundakı elementi silmək
public T removeLast() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("LinkedList is empty");
}
T data = tail.data;
if (size == 1) {
head = null;
tail = null;
} else {
tail = tail.prev;
tail.next = null;
}
size--;
return data;
}
// Verilmiş indeksdəki elementi silmək
public T remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size);
}
if (index == 0) {
return removeFirst();
}
if (index == size - 1) {
return removeLast();
}
Node<T> current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
T data = current.data;
current.prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = current.prev;
size--;
return data;
}
// Verilmiş indeksdəki elementi əldə etmək
public T get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size);
}
Node<T> current;
// Optimize: start from head or tail depending on which is closer
if (index < size / 2) {
current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
} else {
current = tail;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) {
current = current.prev;
}
}
return current.data;
}
// Verilmiş indeksdəki elementi dəyişdirmək
public void set(int index, T data) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size);
}
Node<T> current;
// Optimize: start from head or tail depending on which is closer
if (index < size / 2) {
current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
} else {
current = tail;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) {
current = current.prev;
}
}
current.data = data;
}
// LinkedList-i irəlidən çap etmək
public void printForward() {
Node<T> current = head;
System.out.print("Forward: ");
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " <-> ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
// LinkedList-i geriyə çap etmək
public void printBackward() {
Node<T> current = tail;
System.out.print("Backward: ");
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " <-> ");
current = current.prev;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList<Integer> list = new DoublyLinkedList<>();
// Elementlər əlavə etmək
list.addLast(10);
list.addLast(20);
list.addLast(30);
list.addFirst(5);
list.add(2, 15);
list.printForward(); // Forward: 5 <-> 10 <-> 15 <-> 20 <-> 30 <-> null
list.printBackward(); // Backward: 30 <-> 20 <-> 15 <-> 10 <-> 5 <-> null
// Elementləri silmək
System.out.println("Removed first: " + list.removeFirst());
System.out.println("Removed last: " + list.removeLast());
System.out.println("Removed at index 1: " + list.remove(1));
list.printForward(); // Forward: 10 <-> 20 <-> null
// Elementləri əldə etmək və dəyişdirmək
System.out.println("Element at index 0: " + list.get(0));
list.set(0, 100);
list.printForward(); // Forward: 100 <-> 20 <-> null
}
}
LinkedList vs. Array
| Aspekt | LinkedList | Array |
|---|---|---|
| Yaddaş Yerləşməsi | Non-contiguous | Contiguous |
| Ölçü | Dinamik | Statik (Java-da ArrayList dinamik) |
| Element Əlavə Etmək | O(1) - əvvələ və sona | O(n) - ortalama |
| Element Silmək | O(1) - əvvəldən və sondan | O(n) - ortalama |
| Random Access | O(n) | O(1) |
| Yaddaş İstifadəsi | Hər element üçün əlavə pointer | Yalnız data |
| İmplementasiya | Nisbətən mürəkkəb | Daha sadə |
LinkedList-in İstifadə Sahələri
- Dynamic Memory Allocation: Dinamik yaddaş ayırma
- Implementation of Stacks and Queues: Stack və Queue implementasiyası
- Hash Tables: Hash table-ların collision handling-i
- Undo Functionality: Əməliyyatları geri qaytarmaq
- Music Playlist: Musiqi pleylistləri
- Browser History: Brauzer tarixçəsi
LinkedList-in Mürəkkəbliyi
| Əməliyyat | Singly LinkedList | Doubly LinkedList |
|---|---|---|
| Access | O(n) | O(n) |
| Search | O(n) | O(n) |
| Insert at beginning | O(1) | O(1) |
| Insert at end | O(n) / O(1)* | O(1) |
| Insert at middle | O(n) | O(n) |
| Delete at beginning | O(1) | O(1) |
| Delete at end | O(n) / O(1)* | O(1) |
| Delete at middle | O(n) | O(n) |
*O(1) əgər tail pointer saxlanılırsa
LinkedList-in Java Collections Framework-də İstifadəsi
Java Collections Framework-də java.util.LinkedList class-ı var ki, bu həm List, həm də Deque interface-lərini implement edir:
Koda bax
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class JavaLinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
// List kimi istifadə
list.add("A");
list.add("B");
list.add("C");
list.add(1, "D");
System.out.println("LinkedList: " + list);
// Deque kimi istifadə
list.addFirst("First");
list.addLast("Last");
System.out.println("After addFirst/addLast: " + list);
System.out.println("First element: " + list.getFirst());
System.out.println("Last element: " + list.getLast());
System.out.println("Removed first: " + list.removeFirst());
System.out.println("Removed last: " + list.removeLast());
System.out.println("Final LinkedList: " + list);
}
}